“Meteorological Beast in Our Solar System” – Powerful Stratospheric Winds Measured on Jupiter for the First Time
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
TOPICS:ALMAAstronomyAstrophysicsEuropean Southern ObservatoryGeophysicsJupiterPlanetsPopular
By EUROPEAN SOUTHERN OBSERVATORY MARCH 18, 2021

Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), in which the European Southern Observatory (ESO) is a partner, a team of astronomers have directly measured winds in Jupiter’s middle atmosphere for the first time. By analyzing the aftermath of a comet collision from the 1990s, the researchers have revealed incredibly powerful winds, with speeds of up to 1450 kilometers an hour, near Jupiter’s poles. They could represent what the team have described as a “unique meteorological beast in our Solar System.”
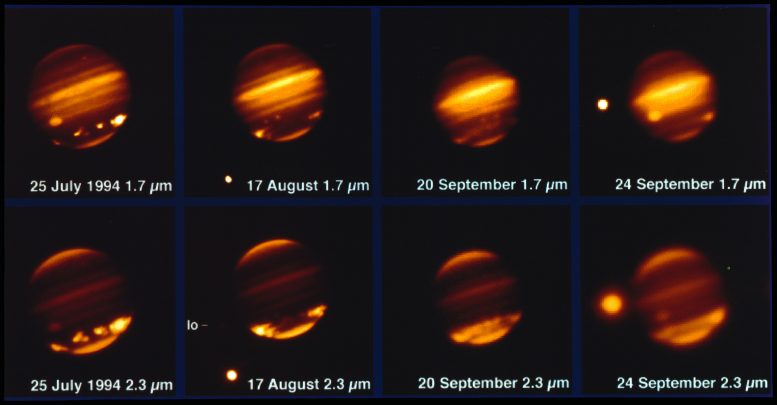

This image, taken with the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope and the IRAC instrument, shows comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 impacting Jupiter in July 1994. Credit: ESO
Jupiter is famous for its distinctive red and white bands: swirling clouds of moving gas that astronomers traditionally use to track winds in Jupiter’s lower atmosphere. Astronomers have also seen, near Jupiter’s poles, the vivid glows known as aurorae, which appear to be associated with strong winds in the planet’s upper atmosphere. But until now, researchers had never been able to directly measure wind patterns in between these two atmospheric layers, in the stratosphere.
These two photos from the ESO La Silla observatory show the individual nuclei of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9, now headed for collision with Jupiter. Credit: ESO
Measuring wind speeds in Jupiter’s stratosphere using cloud-tracking techniques is impossible because of the absence of clouds in this part of the atmosphere. However, astronomers were provided with an alternative measuring aid in the form of comet Shoemaker–Levy 9, which collided with the gas giant in spectacular fashion in 1994. This impact produced new molecules in Jupiter’s stratosphere, where they have been moving with the winds ever since.
A team of astronomers, led by Thibault Cavalié of the Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Bordeaux in France, have now tracked one of these molecules — hydrogen cyanide — to directly measure stratospheric “jets” on Jupiter. Scientists use the word “jets” to refer to narrow bands of wind in the atmosphere, like Earth’s jet streams.
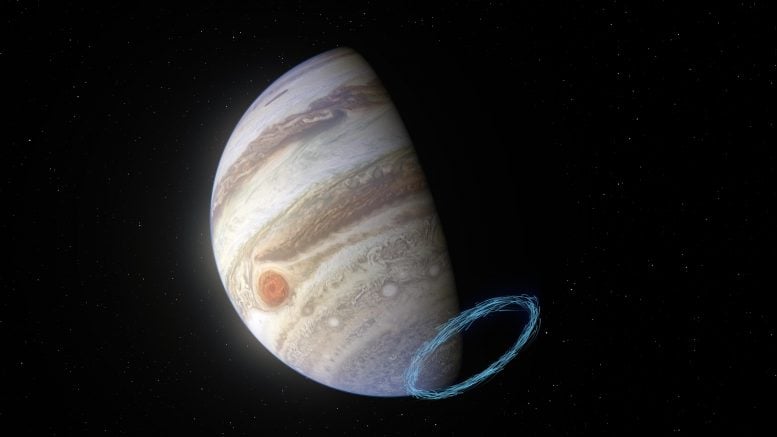

This image shows an artist’s impression of winds in Jupiter’s stratosphere near the planet’s south pole, with the blue lines representing wind speeds. These lines are superimposed on a real image of Jupiter, taken by the JunoCam imager aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
Jupiter’s famous bands of clouds are located in the lower atmosphere, where winds have previously been measured. But tracking winds right above this atmospheric layer, in the stratosphere, is much harder since no clouds exist there. By analyzing the aftermath of a comet collision from the 1990s and using the ALMA telescope, in which ESO is a partner, researchers have been able to reveal incredibly powerful stratospheric winds, with speeds of up to 1450 kilometers an hour, near Jupiter’s poles.
Credit: ESO/L. Calçada & NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
“The most spectacular result is the presence of strong jets, with speeds of up to 400 meters per second, which are located under the aurorae near the poles,” says Cavalié. These wind speeds, equivalent to about 1450 kilometers an hour, are more than twice the maximum storm speeds reached in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot and over three times the wind speed measured on Earth’s strongest tornadoes.
“Our detection indicates that these jets could behave like a giant vortex with a diameter of up to four times that of Earth, and some 900 kilometers in height,” explains co-author Bilal Benmahi, also of the Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Bordeaux. “A vortex of this size would be a unique meteorological beast in our Solar System,” Cavalié adds.
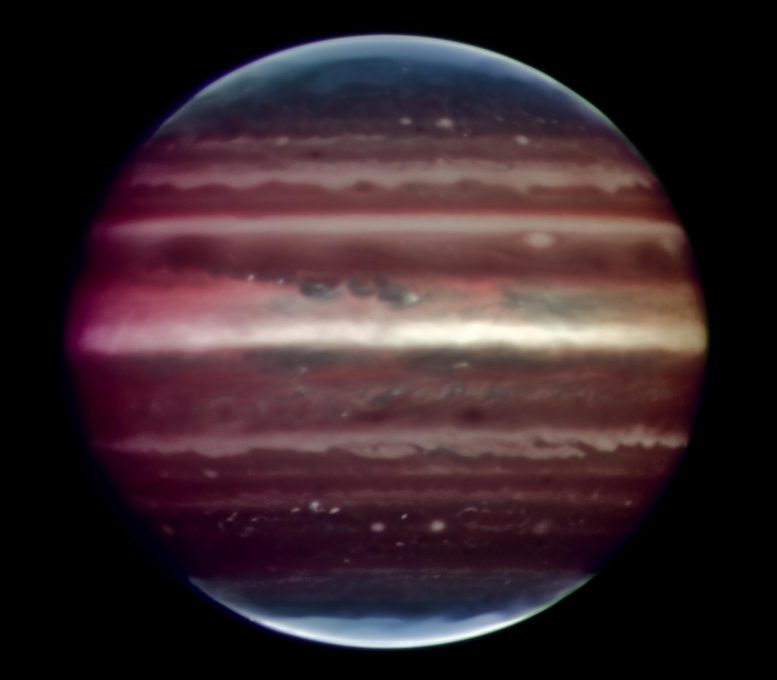

Amazing image of Jupiter taken in infrared light on the night of 17 August 2008 with the Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics Demonstrator (MAD) prototype instrument mounted on ESO’s Very Large Telescope. This false color photo is the combination of a series of images taken over a time span of about 20 minutes, through three different filters (2, 2.14, and 2.16 microns). The image sharpening obtained is about 90 milli-arcseconds across the whole planetary disc, a real record on similar images taken from the ground. This corresponds to seeing details about 300 km wide on the surface of the giant planet. The great red spot is not visible in this image as it was on the other side of the planet during the observations. The observations were done at infrared wavelengths where absorption due to hydrogen and methane is strong. This explains why the colors are different from how we usually see Jupiter in visible-light. This absorption means that light can be reflected back only from high-altitude hazes, and not from deeper clouds. These hazes lie in the very stable upper part of Jupiter’s troposphere, where pressures are between 0.15 and 0.3 bar. Mixing is weak within this stable region, so tiny haze particles can survive for days to years, depending on their size and fall speed. Additionally, near the planet’s poles, a higher stratospheric haze (light blue regions) is generated by interactions with particles trapped in Jupiter’s intense magnetic field.
Credit: ESO/F. Marchis, M. Wong, E. Marchetti, P. Amico, S. Tordo
Astronomers were aware of strong winds near Jupiter’s poles, but much higher up in the atmosphere, hundreds of kilometers above the focus area of the new study, which is published today in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. Previous studies predicted that these upper-atmosphere winds would decrease in velocity and disappear well before reaching as deep as the stratosphere. “The new ALMA data tell us the contrary,” says Cavalié, adding that finding these strong stratospheric winds near Jupiter’s poles was a “real surprise.”
This video shows an artist’s animation of winds in Jupiter’s stratosphere near the planet’s south pole, with the blue lines representing wind speeds. These lines are superimposed on a real image of Jupiter, taken by the JunoCam imager aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft. Credit: ESO/L. Calçada & NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
The team used 42 of ALMA’s 66 high-precision antennas, located in the Atacama Desert in northern Chile, to analyze the hydrogen cyanide molecules that have been moving around in Jupiter’s stratosphere since the impact of Shoemaker–Levy 9. The ALMA data allowed them to measure the Doppler shift — tiny changes in the frequency of the radiation emitted by the molecules — caused by the winds in this region of the planet. “By measuring this shift, we were able to deduce the speed of the winds much like one could deduce the speed of a passing train by the change in the frequency of the train whistle,” explains study co-author Vincent Hue, a planetary scientist at the Southwest Research Institute in the US.
In addition to the surprising polar winds, the team also used ALMA to confirm the existence of strong stratospheric winds around the planet’s equator, by directly measuring their speed, also for the first time. The jets spotted in this part of the planet have average speeds of about 600 kilometers an hour.
The ALMA observations required to track stratospheric winds in both the poles and equator of Jupiter took less than 30 minutes of telescope time. “The high levels of detail we achieved in this short time really demonstrate the power of the ALMA observations,” says Thomas Greathouse, a scientist at the Southwest Research Institute in the US and co-author of the study. “It is astounding to me to see the first direct measurement of these winds.”
This animation of Jupiter was created from real images taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The impact sites of the fragments of comet Shoemaker–Levy 9, which hit Jupiter in 1994, are visible in dark brown in the planet’s southern hemisphere. Credit: ESO/M. Kornmesser, NASA/ESA
“These ALMA results open a new window for the study of Jupiter’s auroral regions, which was really unexpected just a few months back,” says Cavalié. “They also set the stage for similar yet more extensive measurements to be made by the JUICE mission and its Submillimetre Wave Instrument,” Greathouse adds, referring to the European Space Agency’s JUpiter ICy moons Explorer, which is expected to launch into space next year.
ESO’s ground-based Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), set to see first light later this decade, will also explore Jupiter. The telescope will be capable of making highly detailed observations of the planet’s aurorae, giving us further insight into Jupiter’s atmosphere.
More information
Reference: “First direct measurement of auroral and equatorial jets in the stratosphere of Jupiter” by T. Cavalié, B. Benmahi, V. Hue, R. Moreno, E. Lellouch, T. Fouchet, P. Hartogh, L. Rezac, T. K. Greathouse, G. R. Gladstone, J. A. Sinclair, M. Dobrijevic, F. Billebaud and C. Jarchow, 18 March 2021, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202140330
The team is composed of T. Cavalié (Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Bordeaux [LAB], France, and LESIA, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University [LESIA], France), B. Benmahi (LAB), V. Hue (Southwest Research Institute [SwRI], USA), R. Moreno (LESIA), E. Lellouch (LESIA), T. Fouchet (LESIA), P. Hartogh (Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung [MPS], Germany), L. Rezac (MPS), T. K. Greathouse (SwRI), G. R. Gladstone (SwRI), J. A. Sinclair (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, USA), M. Dobrijevic (LAB), F. Billebaud (LAB) and C. Jarchow (MPS).
ESO is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organization in Europe and the world’s most productive ground-based astronomical observatory by far. It has 16 Member States: Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom, along with the host state of Chile and with Australia as a Strategic Partner. ESO carries out an ambitious program focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organizing cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope and its world-leading Very Large Telescope Interferometer as well as two survey telescopes, VISTA working in the infrared and the visible-light VLT Survey Telescope. Also at Paranal ESO will host and operate the Cherenkov Telescope Array South, the world’s largest and most sensitive gamma-ray observatory. ESO is also a major partner in two facilities on Chajnantor, APEX and ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. And on Cerro Armazones, close to Paranal, ESO is building the 39-meter Extremely Large Telescope, the ELT, which will become “the world’s biggest eye on the sky.”
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of ESO, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI). ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
We recommend
- Herschel Solves Mystery of Origin of Water in the Upper Atmosphere of JupiterStaff, SciTechDaily, 2013
- Incredible New Radio Wave Images Show What’s Inside Jupiter’s Storms [Video]Mike ONeill, SciTechDaily, 2019
- ESO Telescope Sees Telltale Signs of a Baby Planet Coming Into ExistenceMike ONeill, SciTechDaily, 2020
- Climate Change Impacts Astronomical ObservationsMike ONeill, SciTechDaily, 2020
- Astronomers Discover Two Distinct Families of Exocomets Around Beta PictorisJames Kelly, SciTechDaily, 2014
- Analysis and Simulation of the Stratospheric Quasi-zero Wind Layer over Korla, Xinjiang Province, ChinaRui Yang et al., Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2019
- First light on an adaptive optics system using a non-modulation pyramid wavefront sensor for a 1.8 m telescopeShengqian Wang et al., Chinese Optics Letters, 2018
- BioMérieux, DiaSorin, GenMark, and Others Receive FDA Clearances in DecemberLeo O'Connor et al., GenomeWeb, 2019
- Numerical simulation of climate response to ultraviolet irradiation forcingXiao et al., Advances in Climate Change Research, 2019
- Effects of Sea-Surface Waves and Ocean Spray on Air–Sea Momentum FluxesTing Zhang et al., Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2018








Comments
Post a Comment